Yellow fever
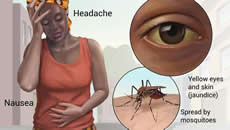 | Yellow fever is a viral infection spread by a particular species of mosquito. It is spread by a species of mosquito common to areas of Africa and South America. Vaccination is recommended before travelling to certain areas. |
- Preventable by vaccine
- Treatment can help, but this condition can’t be cured
- Spreads by animals or insects
- Requires a medical diagnosis
- Lab tests or imaging often required
- Short-term: resolves within days to weeks
How it spreads
- By animal or insect bites or stings
Symptoms
Mild cases cause fever, headache, nausea and vomiting. Serious cases may cause fatal heart, liver and kidney conditions.
- Pain areas: in the abdomen or muscles
- Whole body: chills, fatigue, fever, or loss of appetite
- Gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting
- Also common: bleeding, delirium, headache, or yellow skin and eyes
Treatment
No specific treatment for the disease exists. Efforts focus on managing symptoms and limiting complications.
Supportive care:
Oral Rehydration therapy: Giving fluid by mouth to treat dehydration caused by diarrhoea
Specialists
- Infectious Disease Doctor: Treats infections, including those that are tropical in nature
- Critical Care Doctor: Monitors and treats those in intensive care
- Travel Medicine: Manages health concerns for international travellers
- General Practitioner (GP): Prevents, diagnoses and treats diseases
- Emergency Medicine Doctor: Treats patients in the emergency department
Yellow fever vaccine (PDF file, 302.3 KB) can prevent Yellow fever. After getting the vaccine, you should be given a stamped and signed “International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis” (yellow book). This certificate becomes valid 10 days after vaccination and is good for 10 years. You will need this book as proof of vaccination to enter certain countries.
Yellow fever vaccine is a live, weakened virus. It may be given at the same time as most other vaccines. You should not donate blood for 14 days following the vaccination, because there is a risk of transmitting the vaccine virus through blood products during that period.
You should consider Yellow fever vaccine if you are:
- 9 months through 59 years of age travelling to or living in an area where risk of yellow fever is known to exist or travelling to a country with an entry requirement for the vaccination.
- Laboratory personnel who might be exposed to yellow fever virus or vaccine virus.
NOTE: QUT Medical Centre is an accredited Yellow Fever Clinic. See below for a list of our accredited Yellow Fever practitioners.
KELVIN GROVE: Dr Christine Oo, Dr Goli Bozorgi and Dr Rohan Swaris
GARDENS POINT: Dr Goli Bozorgi
Dosage and Administration
The dose of yellow fever vaccine for children and adults is 0.5mL, to be given by either intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.