Chlamydia
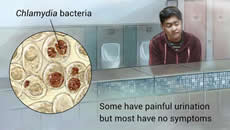 |
Chlamydia also called chlamydia bacteria infection is a common, sexually transmitted infection that may not cause symptoms. Chlamydia affects people of all ages but is most common in young women.
|
What is it?
- The most commonly reported communicable disease in Australia
- Those <30 years are at greater risk
- Frequently asymptomatic
- Simple to test and treat
- Immunity to new infection is not provided by previous infection
Signs and Symptoms
Many people who have Chlamydia are asymptomatic but can still transfer it through sexual contact. Symptoms may include painful urination, penis or vaginal discharge and genital pain. Symptoms can also be gender specific.
| Male | Female |
|
50% have no symptoms
|
75% have no symptoms
|
|
Dysuria
|
Dysuria
|
|
Urethral discharge
|
Vaginal discharge
|
|
Testicular pain
|
Pelvic pain
|
|
Ano-rectal symptoms
|
Intermenstrual bleeding
|
| |
Postcoital bleeding
|
| |
Ano-rectal symptoms
|
Diagnosis
| Male | Female |
|
First pass urine
|
Endocervical swab
|
|
Ano-rectal swab
|
Self-collected vaginal swab
|
|
Pharyngeal swab
|
First pass urine
|
| |
Ano-rectal swab
|
Treatment
- Treated with antibiotics
- Special treatment situations include pregnant women, allergies and those with anal coinfection
- If Chlamydia is not treated it can lead to serious long-term health problems such as infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease
Recommended follow-up
- Advise no sexual contact for 7 days after treatment is administered
- Re-infection is common, re-testing at three-month to detect re-infection
- Consider testing for other STI's at three-month visit, if not undertaken at first presentation or retesting post window period
Contact tracing
- Partners should be traced for 6 months
- Contacting all sexual contacts during potential time of infection
For more information
Information about Chlamydia in other languages
